Understanding the Education Systems in the UK, USA, Germany, and France
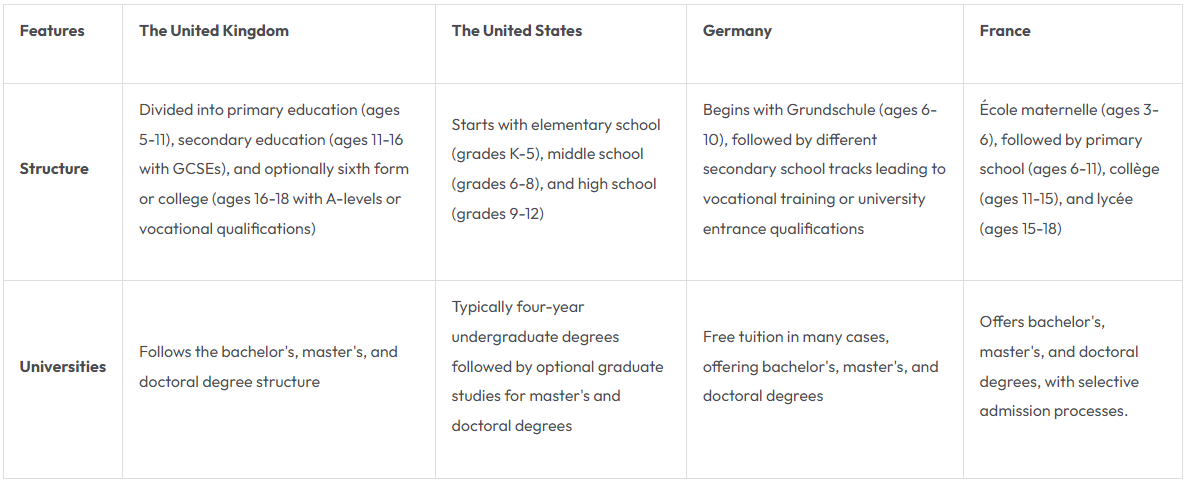
The education systems in the United Kingdom, the United States, Germany, and France exhibit both similarities and distinctive features shaped by historical, cultural, and social factors. In the United Kingdom, education progresses through primary and secondary stages, culminating in A-levels or vocational qualifications before university. The United States divides schooling into elementary, middle, and high school phases, followed by undergraduate and optional graduate studies. Germany’s system includes early differentiation into vocational or university-bound tracks after primary education, emphasizing free higher education opportunities. Meanwhile, France structures education through distinct stages, leading to competitive university admissions for bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. Each system reflects national priorities in preparing students for further academic or vocational pursuits, highlighting diverse approaches to education across these nations.

The education systems in these countries have some similarities but also significant differences:
⇒ The United Kingdom (UK):
For those who are new to the UK or are unfamiliar with its structure, the process of navigating the education system can be particularly challenging. The United Kingdom provides a wide variety of educational opportunities, extending from early childhood education to college and beyond. It is imperative that students, parents, and educators understand this system. This article will offer an exhaustive overview of the UK education system, including its main stages, examination boards, support services, and more.
Understanding the Key Stages: The UK education system is divided into several key stages, each catering to specific age groups and educational needs. These stages include the Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS), Primary Education, Secondary Education, Further Education, and Higher Education. We delve into each stage, highlighting its objectives and typical age ranges.
- Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS): This stage is for children aged 0-5 and focuses on learning through play and exploration. Nursery schools, preschools, and reception classes in primary schools are part of this stage.
- Primary Education: Primary education starts from age 5 and continues until age 11. Key stages 1 and 2 are part of primary education.
- Secondary Education: Secondary education begins at age 11 and lasts until age 16. At the end of Key Stage 4, students typically take their GCSEs (General Certificate of Secondary Education).
- Further Education: After completing compulsory education, students can choose to continue their studies in further education. This can include studying for A-levels, vocational qualifications, or apprenticeships. Colleges and sixth-form colleges provide further education.
- Higher Education: Higher education includes universities and colleges offering degree-level courses. Undergraduate degrees typically last three to four years. Postgraduate degrees (master’s and PhD) follow undergraduate studies.
Transitioning to Higher Education
For many students ( especially the international students), transitioning to higher education in the UK marks a significant milestone in their academic journey. The insights into the application process for universities and colleges is provided through UCAS (Universities and Colleges Admissions Service). From crafting a compelling personal statement to securing academic references, we, at BCES, offer practical tips to help applicants navigate this crucial stage.
Financial Considerations
Financing education is a key consideration for many students and their families. We discuss the funding mechanisms for education in the UK, including government grants, tuition fees, and student loans. By understanding the financial aspects of education, students can make informed decisions about their educational pursuits without being hindered by financial constraints.
Support Services for Students
Schools and universities in the UK offer a range of support services to help students thrive academically, emotionally, and socially. We shed light on these services, including counseling, disability support, academic tutoring, and career guidance. Understanding the support available can empower students to overcome challenges and make the most of their educational journey.
The Cost of Education in the UK
The Cost of Studying in the United Kingdom can be expensive, and the cost varies depending on several factors, including the level of education, the location of the university, your chosen course of study, and your lifestyle.
Undergraduate (UG) Program Costs in the UK
UK undergraduate tuition fees range from £10,000 to £25,000, with medical-based programs costing between £20,000 and £45,000, with additional expenses like accommodation and living costs.
Postgraduate (PG) Program Costs in the UK
UK postgraduate fees have increased, with average annual costs ranging from £12,000 to £30,000, and doctoral degrees from £15,000 to £25,000.
Average Cost of Living in UK for Indian Students
The cost of living in the UK varies depending on factors such as mobile phone bills, food shop expenses, TV licenses, transportation, clothing, utility bills, internet and broadband services, dining out, entertainment, gym or fitness memberships, healthcare expenses, personal care and toiletries, insurance, socializing and leisure activities, and miscellaneous expenses. Mobile phone bills can range from £15 to £30 per month, while food shop expenses can range from £200 to £300 per month. A TV license is required for live TV or use the BBC iPlayer, and public transportation costs vary across cities. Clothing expenses can range from £50 to £100 per month, while utility bills can range from £80 to £150. Personal care expenses can range from £20 to £30 per month.
Intake in the UK for Higher Education for International Students:
- The Spring/January intake: It is a significant period for studying abroad in the UK which represents the second admission session for institutions there, usually commencing in January and ending in early May. The application period for January entry courses runs from June to September.
- The Summer/May intake: It is a condensed study abroad program, typically spanning from May to July or August. Although less prevalent than the Fall and Spring intakes, certain universities provide specialized summer programs or courses tailored for overseas students.
- The Fall/September intake: This is a prominent study abroad period provided by universities worldwide. The duration of the event usually commences in late August or early September and concludes in late December.
⇒ The United States(USA) :
Typically, students in the USA begin their education when they turn 6. The US education comprises a categorized system which starting from the elementary education goes upto high school before a student enters higher education in colleges or universities.
Distribution of the US education system in 4 categories is as under:
- Primary Education: The primary education covers the elementary school level where the students complete classes 1-4 between the age group of 6-11 years.
- Middle Education: Between the age of 11-14 years, the students complete classes 6-8 and this level is considered middle /junior school level.
- Secondary Education: Next comes the high school level, where the students complete 9-12 grades in the age group of 14-18 years.
- Tertiary Education: Once the students completes high school education from the age of 18, their higher level education is considered complete and they get enrolled into colleges or universities.
What does the USA have to offer after Secondary Education.
Once the students complete secondary education in the USA, they come across a variety of options for further studies, which clearly depends upon their interests, career goals and individual situations. Every option comes with a unique opportunity for personal and academic growth and prepares the students for further success in studies as well as the workplace. The options for further studies are as under:
- Undergraduate Studies: There are plenty of students who choose to pursue undergraduate studies at colleges or universities. These generally lead to a Bachelor’s degree and typically lasts four years. There is a wide range of courses available for students to choose from like, sciences, engineering, business, liberal arts and so on.
- Community College: Also known as Junior colleges or two-year colleges, the community colleges offer two-year associate degree programs. You can also get certificate and diploma programs. This is a high choice among any students as these institutions provide a more flexible schedule and more affordable tuition fees.
- Trade Schools and Vocational Programs: Trade schools and vocational programmes are available for students who want to work in certain skills or vocational fields. Most of the time, these programmes teach and train students by doing research in areas like automobile technology, cooking, cosmetics, healthcare, and more. They can get badges, certificates, or associate degrees in any subject they want.
- Gap Year Programs: Some of the students are more fond of cultural immersion, gaining real life world experience and getting opportunities for personal development. Such students always opt for a gap year after high school to accomplish their hobbies like travel, work, volunteer etc.
- International Studies: International students may choose to do their first year of college in the United States. They can apply straight to US schools and universities or take part in exchange programmes run by organizations in their home countries or around the world.
Why is Studying in the USA a great option for international students?
Quality of Education: Some of the world’s best colleges are in the United States. These schools are known for having tough academic programmes and great teachers. Our school has cutting-edge programmes for students in many subjects, such as business, engineering, medicine, and the arts. These courses are meant to challenge and inspire students. It is important for many schools to focus on cutting-edge study, which gives students the chance to learn from well-known experts in their fields.
Cultural Immersion: The USA has a lot of cultural experiences, festivals, and events, from lively towns to beautiful nature landscapes. You can become immersed in American culture while still keeping your own culture. Universities in the United States are places where people from many countries come together to learn. They create a lively and friendly environment for learning. You will be able to learn new things while studying with students from other countries if you take part in this course. This will help you understand other cultures better and interact more effectively.
Varied Learning Environment: When you study in the US, you’ll be in a culturally varied setting where you’ll connect with other students from different countries, backgrounds, and points of view. This will make your learning experience better. Many international students from a wide range of countries and backgrounds come to the US to go to college. Every day, college schools in the US have students from 150 to 170 different countries.
A Broad Range of Programmes: The USA has a huge selection of programmes and courses for all kinds of students, whether they are interested in the liberal arts, STEM areas, business, or something else. There are many courses to choose from, and you can make your own learning plan. If you aren’t sure what major you want to choose, you might want to look into going to schools in the United States.
Financial Aid: International students can get scholarships and other forms of help. Don’t let money problems stop you from moving forward! A lot of American schools offer grants and other forms of financial aid that are specifically made for international students. The knowledgeable advisors at EduFund can help you get the financial aid you need and look into grant options, making your dream of studying in the US a reality.
So how much will it cost to study in the USA?
A student who wishes to do Undergraduate degree from the USA needs an overall budget of 35-40 lakhs, which includes your fees, living expenses, whereas for acquiring a master’s degree from the USA, you need to have an overall budget of 30-35 lakhs. However, there are two categories of Universities in the US – Private and State/Public. The cost of education in the USA at a public/state university is fairly lesser than that of a private institution. Your cost on tuition fees depends on the type of programs and university or school you opt for.
⇒ Germany:
Germany offers diverse higher education institutions, including research-focused universities, practical universities of applied sciences, and specialized colleges of art and music. Prospective students must meet specific academic qualifications and language proficiency, with many programs requiring German language skills. The application process often involves services like Uni-Assist, and deadlines vary by semester. Financially, most public universities have low or no tuition fees, but students should budget for living expenses and health insurance. Scholarships such as those from DAAD and Erasmus+ can provide financial support. Securing accommodation early, learning German, and understanding local bureaucracy are crucial for smooth integration. Engaging in student life, joining clubs, and networking can enhance the experience. Preparation, research, and cultural adaptation are vital for navigating and thriving in Germany’s education system.
Here are some essential tips to help prospective students understand and successfully navigate the system:
Understanding the Structure
Types of Higher Education Institutions:
- Universities: Focus on research and offer a wide range of disciplines. Offer a broad spectrum of academic disciplines, including humanities, natural sciences, law, and medicine. Provides Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Ph.D. programs. Put strong emphasis on theoretical knowledge and research.
- Universities of Applied Sciences: More practice-oriented, focusing on engineering, business, and social sciences. Concentrate on engineering, business, social sciences, and design. Provides Primarily Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees and is in close links with industry and practical training.
- Colleges of Art, Film, and Music : Specialized institutions for creative fields. Courses in fine arts, design, performing arts, and media. Cater into Bachelor’s, Master’s, and some offer Ph.D. programs with strong emphasis on artistic and practical skills.
Degree Programs:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Typically 3-4 years. Combines theoretical learning with practical modules and requires completion of 180 to 240 ECTS credits.
- Master’s Degree: 1-2 years, following a Bachelor’s. Gives in-depth study of a specialized field, often including a thesis. This requires completion of 60 to 120 ECTS credits.
- Ph.D. (Doctorate): Involves independent research, usually 3-5 years. Involves original research leading to a dissertation. Conducted under the supervision of a professor and may include teaching responsibilities.
Admission Requirements
Germany’s higher education structure is diverse and well-regarded, consisting of three main types of institutions: universities, universities of applied sciences, and colleges of art, film, and music. Traditional universities (Universitäten) focus on a broad range of academic disciplines and emphasize research, offering Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Ph.D. programs. Universities of applied sciences (Fachhochschulen) are more practice-oriented, specializing in fields like engineering, business, and social sciences, and typically offer Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees. Colleges of art, film, and music (Kunst- und Musikhochschulen) cater to creative fields, providing specialized training in fine arts, design, music, and performing arts. This system allows students to choose an educational path that aligns with their academic interests and career goals, ensuring a comprehensive and practical approach to higher education.
- Academic Qualifications:
Equivalent to the German high school diploma.
Recognition of foreign qualifications can be checked via the anabin database.
- Language Proficiency:
German: Most programs are in German; hence, proficiency (B2 or C1 level) is required. Tests include TestDaF, DSH, or Goethe-Institut exams.
English: Increasing number of programs in English; IELTS or TOEFL scores might be needed.
- Application Process:
Uni-Assist: Many universities use this service to evaluate international applications.
Direct Application: Some universities accept direct applications.
Deadlines: Typically mid-July for winter semester and mid-January for summer semester.
Financial Considerations
Financial considerations in Germany encompass a range of factors important for both residents and businesses. Germany’s robust economy, characterized by a strong industrial base and a thriving export sector, influences personal and corporate financial decisions. Individuals need to navigate a well-developed banking system, understand taxation policies, and consider social security contributions, which include health insurance, pensions, and unemployment benefits. For businesses, financial considerations include corporate tax rates, labor costs, and regulatory compliance, which are essential for maintaining profitability and competitiveness. Additionally, Germany’s stable economic environment and favorable investment climate attract foreign investments, impacting financial planning and opportunities within the country.
- Tuition Fees:
Most public universities do not charge tuition fees for undergraduate studies.
Some states charge fees for non-EU students; check specific university requirements.
- Cost of Living:
Monthly expenses average €800-€1,200, including rent, food, transportation, health insurance, and other personal expenses.
- Scholarships and Funding:
DAAD Scholarships: Wide range of scholarships for international students.
Erasmus+: For EU students.
Deutschlandstipendium: Merit-based scholarships.
⇒ France:
The French education system is renowned for its structured and rigorous approach, characterized by distinct stages designed to provide a comprehensive academic foundation. Beginning with École Maternelle (preschool), which prepares children aged 3 to 6 for formal education, the system progresses through École Élémentaire (elementary school), where compulsory education begins and foundational skills in subjects like mathematics, French language, and sciences are cultivated.
The education system in France is structured into several stages, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Preschool: This is not compulsory but is widely attended by children aged 3 to 6.
- Elementary School: Compulsory for children aged 6 to 11, covering CP (Cours Préparatoire), CE1 (Cours Élémentaire 1), CE2 (Cours Élémentaire 2), CM1 (Cours Moyen 1), and CM2 (Cours Moyen 2).
- Middle School: Compulsory education continues here for ages 11 to 15, covering grades 6 to 9 (6ème to 3ème).
- High School: Non-compulsory education from ages 15 to 18, leading up to the Baccalauréat (commonly known as the Bac), which is a prerequisite for higher education.
- Higher Education: Includes universities and specialized schools. The higher education system is divided into public universities, Grandes Écoles (elite higher education institutions), and specialized schools (like art schools or engineering schools).
Financial Considerations: Studying in France can vary greatly in cost depending on several factors such as your nationality, the type of institution you attend, and your chosen program of study. Here are some general points to consider:
- Public Universities: For students from within the EU/EEA or Switzerland, tuition fees are relatively low, often around €170 to €650 per year for undergraduate programs, and slightly higher for master’s programs. For non-EU/EEA/Swiss students, fees can range from €2,770 to €3,770 per year for bachelor’s programs and up to €3,770 to €17,000 per year for master’s programs.
- Grandes Écoles and Private Institutions: These institutions tend to have higher tuition fees compared to public universities. Costs can vary widely depending on the school and program, but fees can range from €3,000 to €20,000 per year or more.
- Living Expenses: This will depend on the city you live in and your lifestyle, but on average, students should budget around €800 to €1,200 per month to cover accommodation, food, transport, and other expenses.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: There are various scholarships available for international students, both from the French government and other organizations, which can significantly reduce the cost of studying in France.
France generally has two main intakes for international students:
- Fall Intake (September/October): This is the primary intake for most universities and higher education institutions. The majority of programs, especially at public universities and Grandes Écoles, begin in the fall. The application period for this intake usually starts in November of the previous year and can extend until April or May, depending on the institution and program.
Spring Intake (January/February): Some institutions offer a secondary intake in the spring. This intake is less common and typically includes fewer programs, mainly at private institutions or specialized schools. The application period for the spring intake usually opens around September or October of the previous year.